There is potential for anti-neonatal Fc receptor (anti-FcRn) technology to help a broad range of people impacted by autoimmune diseases. Over 2 million people are estimated to be living with conditions mediated by harmful immunoglobulin G (IgG) autoantibodies.


IgG autoantibodies mediate autoimmune disease pathogenesis.
In healthy people, IgG antibodies recognize and bind to foreign substances, marking them for destruction. In many autoimmune diseases, however, harmful IgG autoantibodies develop, triggering a harmful immune response where they recognize and bind to normal healthy tissue.

Harmful autoantibodies

FcRn promotes recycling of IgG antibodies.
FcRn maintains levels of IgG in circulation by preventing IgG degradation.
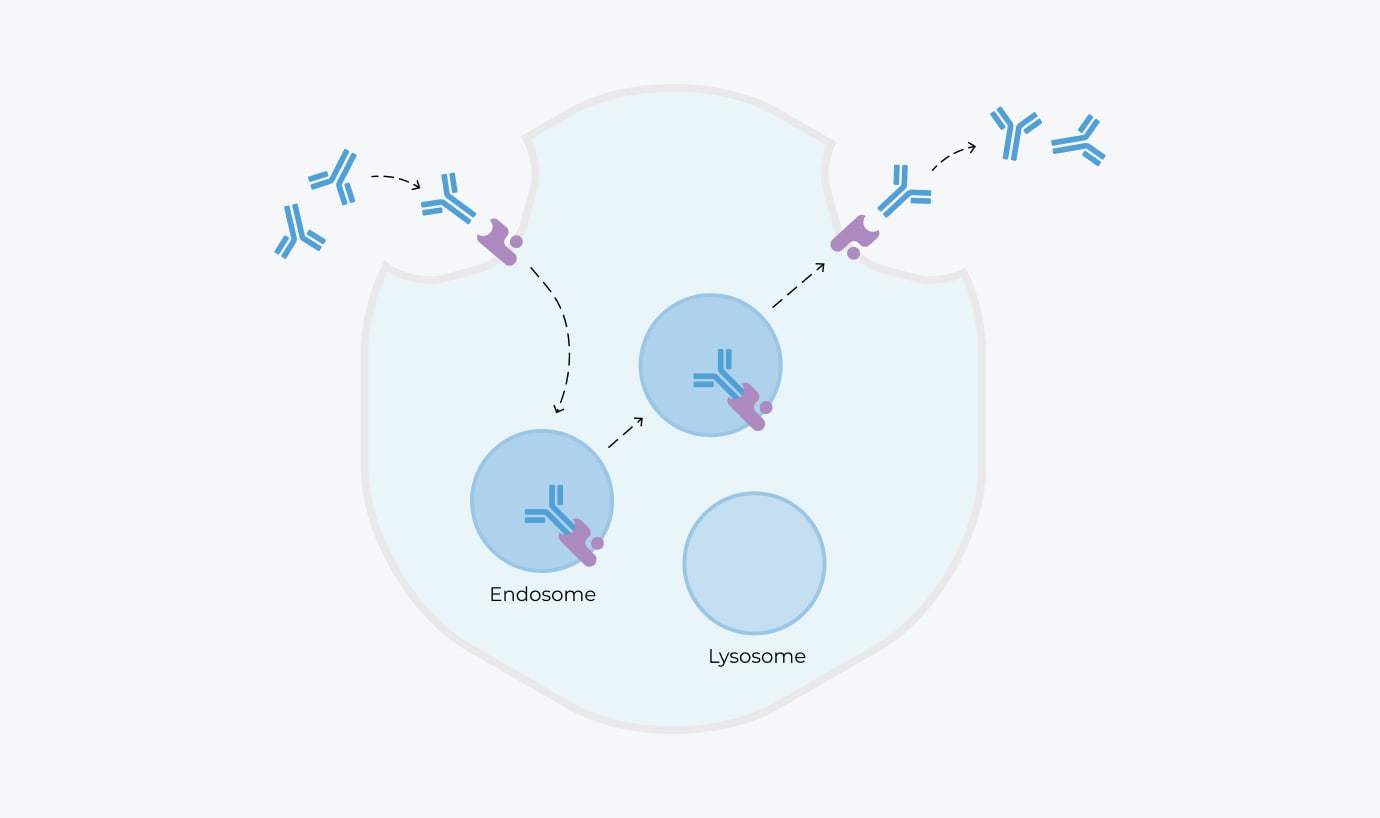

Harmful autoantibodies

FcRn

Our investigational therapies, IMVT-1402 and Batoclimab, inhibit FcRn, promoting IgG degradation.
IMVT-1402 and Batoclimab promote the removal of harmful autoantibodies by binding to FcRn, leading to IgG degradation.
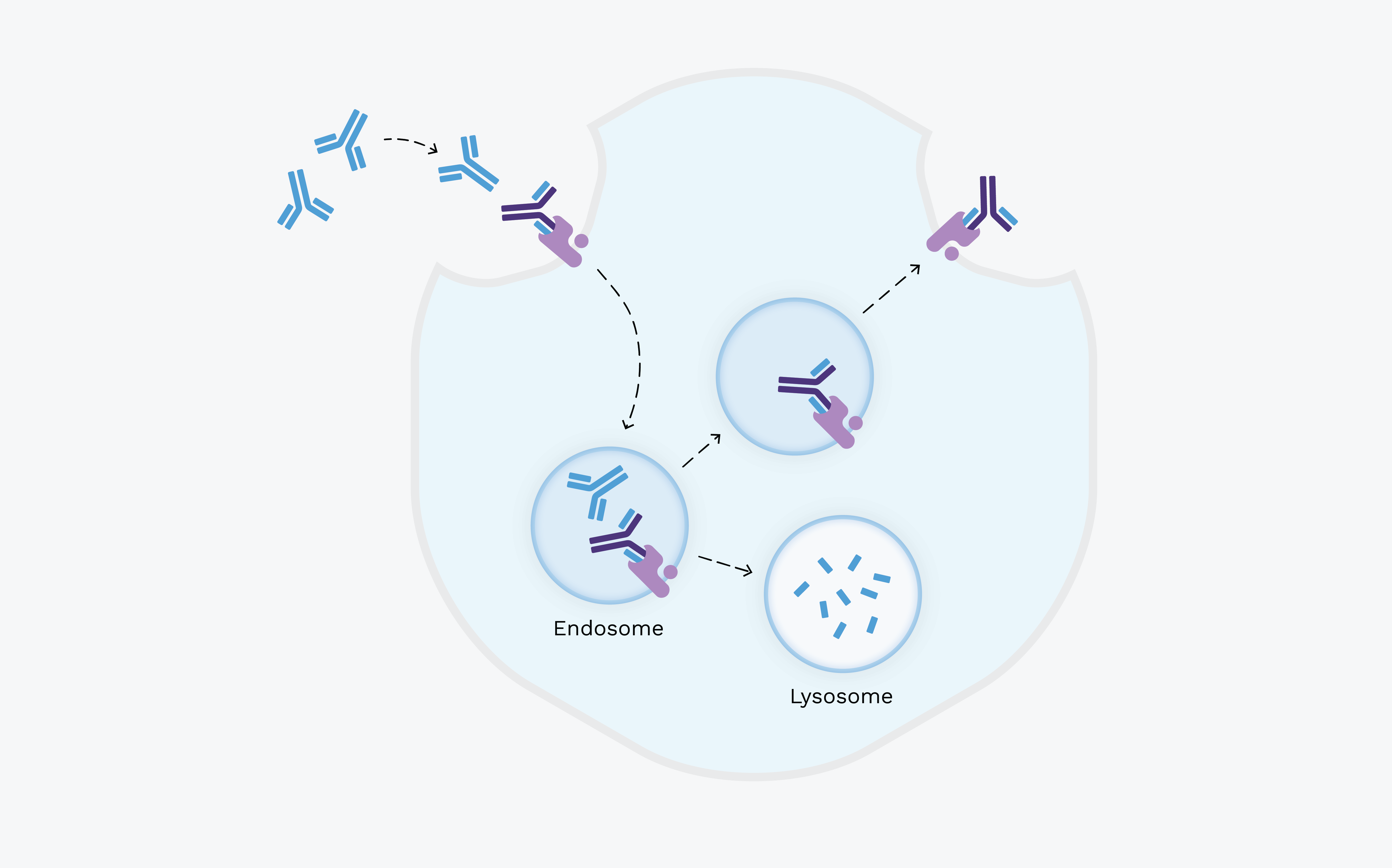

Harmful autoantibodies

FcRn

Batoclimab
The figure above illustrates the proposed mechanism of action for batoclimab, which is also representative of the mechanism of action for IMVT-1402.